1984 North Indian Ocean cyclone season
| 1984 North Indian Ocean cyclone season | |
|---|---|
 Season summary map | |
| Seasonal boundaries | |
| First system formed | May 23, 1984 |
| Last system dissipated | December 10, 1984 |
| Strongest storm | |
| Name | Cyclone Three |
| • Maximum winds | 215 km/h (130 mph) (3-minute sustained) |
| • Lowest pressure | 973 hPa (mbar) |
| Seasonal statistics | |
| Cyclonic storms | 4 |
| Total fatalities | 430 |
| Total damage | Unknown |
| Related articles | |
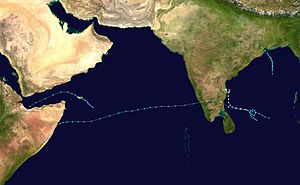
The 1984 North Indian Ocean cyclone season was part of the annual cycle of tropical cyclone formation. The season has no official bounds but cyclones tend to form between April and December. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northern Indian Ocean. There are two main seas in the North Indian Ocean—the Bay of Bengal to the east of the Indian subcontinent and the Arabian Sea to the west of India. The official Regional Specialized Meteorological Centre in this basin is the India Meteorological Department (IMD), while the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) releases unofficial advisories. An average of five tropical cyclones form in the North Indian Ocean every season with peaks in May and November.[1] Cyclones occurring between the meridians 45°E and 100°E are included in the season by the IMD.[2]
Systems
[edit]Tropical Storm One (1A)
[edit]| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | May 23 – May 28 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 85 km/h (50 mph) (1-min); 990 hPa (mbar) |
On May 23 a tropical disturbance developed 180nm (333km) southwest off the island of Socotra. The disturbance moved slowly northwestward as it developed into a tropical depression on May 24, as the system gradually strengthened to a tropical storm on May 26 and being designated 01B by the JTWC. Shortly after being designated, 01B began a gradual turn to the west, then southwest as it entered the Gulf of Aden. 01B attained its peak intensity of 50 mph early on May 27, before weakening until making landfall 35 nm (65km) west of Berbera, Somalia as a 40 mph tropical storm early on May 28. The storm rapidly dissipated overland that same day. There were no reports of damages or deaths from the storm. [3]
The storm was not tracked by the IMD.
Tropical Storm Two (2B)
[edit]| Very severe cyclonic storm (IMD) | |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | October 9 – October 14 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 120 km/h (75 mph) (3-min); 980 hPa (mbar) |
A broad and disorganized area of convection was first detected on October 9 in the north-central Bay of Bengal. The disturbance developed into a tropical depression on October 10. The depression moved north into very favorable upper-level and shear conditions. The JTWC subsequently upgraded the depression into a tropical storm, being designated as 02B. However, land interaction and outflow from a developing Tropical Storm Susan in the South China Sea inhibited any further development into a stronger system. 02B then moved slightly northwest as it attained its peak intensity of 50 mph, This was short-lived as strong upper-level shear began impacting the storm, gradually weakening it until making landfall 10nm (19 km) south of Balasore on October 14, before rapidly weakening overland and disspating that same day. Heavy rains were reported, but death and damage figures are unknown.[3]
Cyclone Three (3B)
[edit]| Extremely severe cyclonic storm (IMD) | |
| Category 2 tropical cyclone (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | November 9 – November 15 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 215 km/h (130 mph) (3-min); 975 hPa (mbar) |
A large disturbance was first noticed by the JTWC west of Sumatra on November 5. The disturbance moved slowly northwestward with little or no change in organization until November 9, when it finally developed into a tropical depression. The depression slowly intensified into a tropical storm late on November 10, and the JTWC designated it 03B. 03B then began to rapidly intensify, going from a 40 mph tropical storm to a 80 mph cyclone in less than 24 hours as it began turning north. Strengthening slowed down as it peaked as a 100 mph category 3 cyclone on November 13, before just stalling offshore Sriharikota. 03B then began being impacted by upwelling and a dramatic increase in wind shear on November 14, before being reduced to a mere convectionless low-level circulation as it made landfall just south of Nellore on November 15 and dissipating thereafter.[3]
Due to the storm's stall, Storm surge of 20 ft hit the nearby village of Durgarajupatnam which led to coastal inundation up to 3 km inland. Nearly 100,000 livestock were killed by the storm and 400,000 houses were destroyed in Andhra Pradesh. In nearby Tamil Nadu, the storm brought moderate damages killing 54 people.[3]
Cyclone Four (4B)
[edit]| Extremely severe cyclonic storm (IMD) | |
| Category 1 tropical cyclone (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | November 27 – December 8 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 215 km/h (130 mph) (3-min); 973 hPa (mbar) |
A large area of convection formed in the southwestern area of the Bay of Bengal on November 20. Over the next week, the disturbance moved in a semi-circular path, eventually developing into a tropical depression on November 27. The depression gradually strengthened into a tropical storm on November 28, 04B then began a two day clockwise loop in the central Bay of Bengal, strengthening into a category 1 cyclone on November 30, eventually peaking as a 85 mph cyclone as it made landfall 40 nm (70km) north of Nagapattinam on December 1. 04B then rapidly weakened overland before restrengthening back into a tropical depression over the eastern Arabian Sea on December 2. 04B reattained tropical storm status late on December 3, as it gradually restrengthened into a 70 mph tropical storm on December 5. 04B kept this intensity for a day as shear increased as it approached southern Somalia, making landfall as a dissipating tropical storm on December 7. The system fully dissipated as it reemerged into the Arabian Sea on December 8.[3]
See also
[edit]- North Indian Ocean tropical cyclone
- 1984 Atlantic hurricane season
- 1984 Pacific hurricane season
- 1984 Pacific typhoon season
- Australian cyclone seasons: 1983–84, 1984–85
- South Pacific cyclone seasons: 1983–84, 1984–85
- South-West Indian Ocean cyclone seasons: 1983–84, 1984–85
References
[edit]- ^ "Frequently Asked Questions: What is the annual frequency of Cyclones over the Indian Seas? What is its intra-annual variation?". India Meteorological Department. 2012. Archived from the original on May 21, 2015. Retrieved June 8, 2012.
- ^ "Bulletins Issued by Regional Specialized Meteorological Centre (RSMC) – Tropical Cyclones, New Delhi" (PDF). India Meteorological Department. May 25, 2009. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2012-04-12. Retrieved July 16, 2012.
- ^ a b c d e 1984 Annual Tropical Cyclone Report (PDF) (Report). Joint Typhoon Warning Center. pp. 135, 145. Retrieved December 6, 2018.
External links
[edit]- India Meteorological Department
- Joint Typhoon Warning Center Archived 2015-08-09 at the Wayback Machine